Empirical Supported Treatment for Trauma
Posted by Sam McManigle

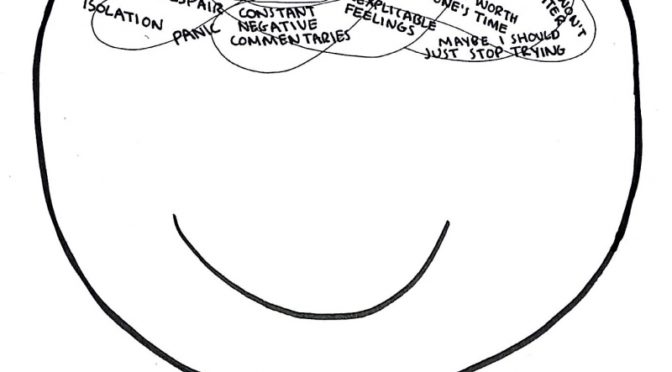
Trauma can be a devastating experience that can have a lasting impact on a person’s life. Symptoms of trauma can include flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, depression, and difficulty sleeping. In some cases, trauma can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a serious mental health condition that can significantly impair a person’s ability to function. There are a number of empirical supported treatments available for trauma.
Some of the most effective treatments include:
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is a type of therapy that uses eye movements, taps, or tones to help people process traumatic memories. EMDR is a relatively new treatment, but it has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD in a number of studies.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that focuses on changing the way people think and behave. CBT can be used to help people with trauma learn how to manage their symptoms and cope with stress.
- Accelerated resolution therapy (ART) is a newer type of therapy that is similar to EMDR. ART uses a combination of eye movements, tapping, and other techniques to help people process traumatic memories.
In addition to these specific treatments, there are a number of other things that can help people who have experienced trauma. These include:
- Support groups: Support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for people to share their experiences and learn from others who have been through similar experiences.
- Yoga and meditation: Yoga and meditation can help people to relax and reduce stress. They can also help people to focus on the present moment and let go of negative thoughts and emotions.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine treatment that has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD.
Furthermore If you have experienced trauma, it is important to seek help from a qualified mental health professional. There are a number of effective treatments available that can help you to heal and recover.
Other treatments for trauma
In addition to the treatments listed above, there are a number of other treatments that may be helpful for people who have experienced trauma. These include:
- Group therapy: Group therapy can provide a safe and supportive environment for people to share their experiences and learn from others who have been through similar experiences.
- Art therapy: Art therapy can help people to express their emotions and trauma in a safe and creative way.
- Music therapy: Music therapy can help people to relax and reduce stress. It can also help people to express their emotions and trauma in a safe and creative way.
- Hypnosis: Hypnosis can be used to help people access and process traumatic memories.
- Animal-assisted therapy: Animal-assisted therapy can help people to reduce stress and anxiety. It can also help people to feel more connected and supported.
The best treatment for trauma will vary depending on the individual’s needs and preferences. It is important to talk to a qualified mental health professional to find the treatment that is right for you.
Read More
 View Our Locations
View Our Locations Request Appointment
Request Appointment